What is sickle cell disease
Sickle cell disease is a genetic blood disorder that affects millions of people worldwide.
It is caused by a mutation in the HBB gene, which provides instructions for making a protein called hemoglobin.
Hemoglobin is responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body.
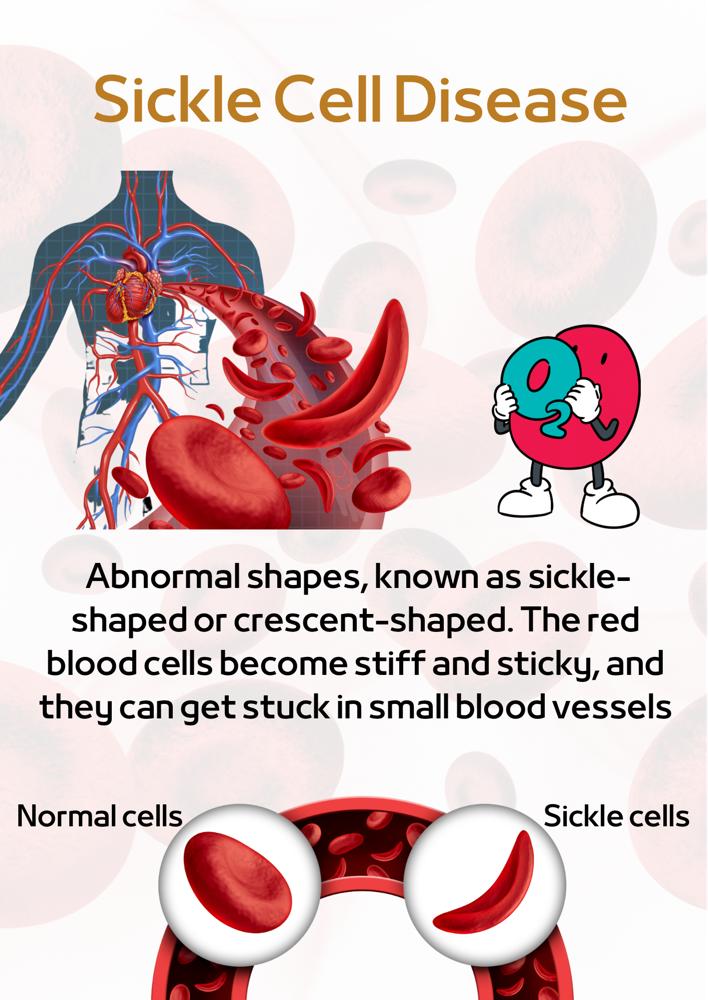
In sickle cell disease, the mutation causes hemoglobin to form abnormal shapes, known as sickle-shaped or crescent-shaped.
These abnormal shapes cause the red blood cells to become stiff and sticky, and they can get stuck in small blood vessels.
This can block the flow of blood and oxygen to various parts of the body, causing pain and damage to organs and tissues.
What causes sickle cell disease
People with sickle cell anemia inherit the disease from their biological parents.
In sickle cell anemia, the gene that helps make normal red blood cells mutates, or changes.
People who inherit the mutated hemoglobin protein gene from both biological parents have sickle cell anemia.
People who inherit the mutated gene from one biological parent have the sickle cell trait.
Symptoms of sickle cell disease
Symptoms of sickle cell disease can range from mild to severe, and they can vary from person to person. Common symptoms include:
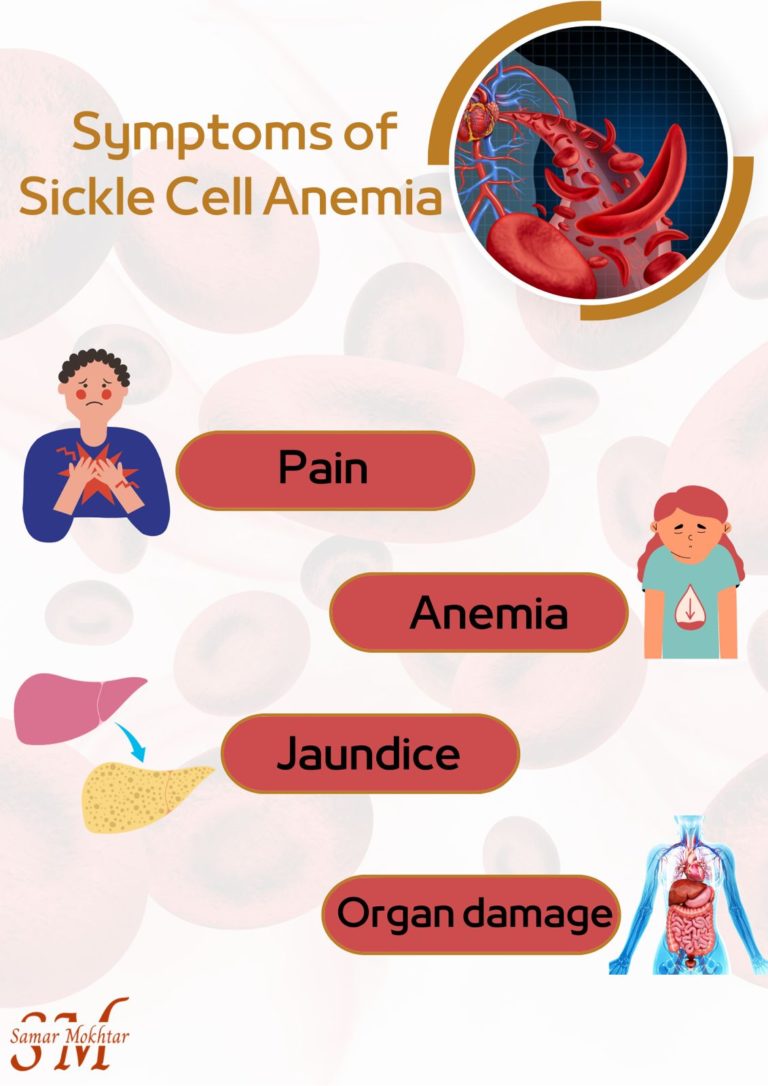
Pain: This is the most common symptom of sickle cell disease. It can occur anywhere in the body and can range from mild to severe.
Pain can be sudden or chronic, and it can last for a few hours to a few days.
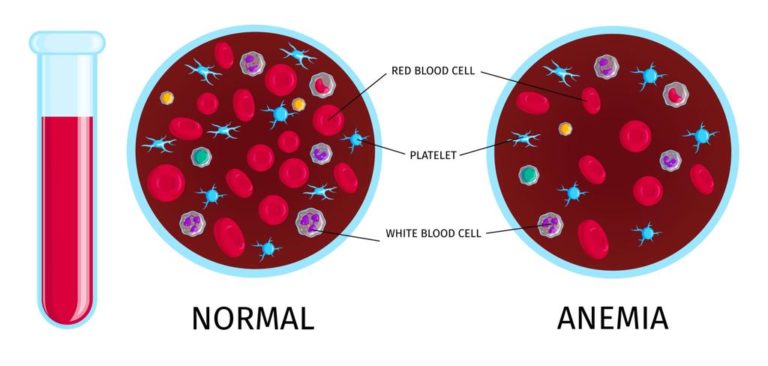
Anemia: Sickle cell disease can cause anemia, a condition in which the body doesn’t have enough red blood cells to carry oxygen to the rest of the body.
Anemia can cause fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, paleness and fast heartbeat.
Jaundice: Sickle cell disease can cause the breakdown of red blood cells, which releases a substance called bilirubin into the blood.
When there is too much bilirubin in the blood, it can cause yellowing of the skin and eyes, known as jaundice.
Organ damage: Over time, sickle cell disease can cause damage to organs such as the spleen, kidneys, and liver.
Treatment for sickle cell disease
Treatment for sickle cell disease includes managing the symptoms and preventing complications. This may include:
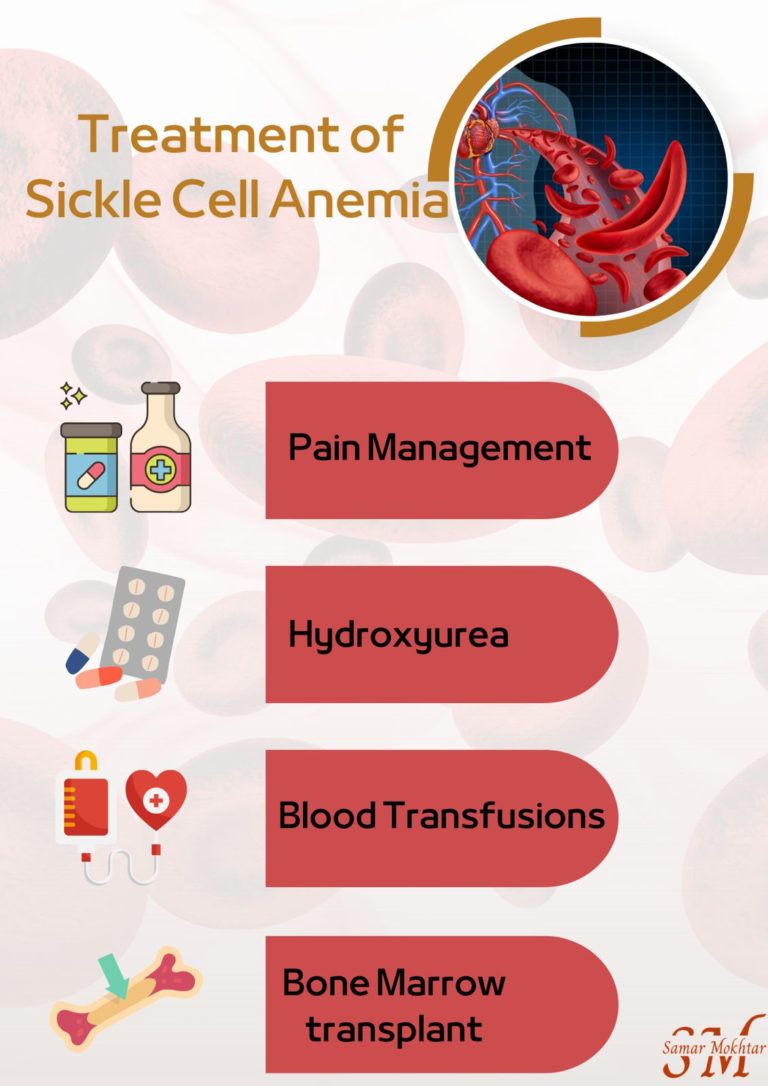
Pain management: Pain can be managed with over-the-counter or prescription pain medication, as well as other treatments such as heat or cold therapy, massage, or relaxation techniques.
Hydroxyurea: This medication can help reduce the frequency and severity of pain episodes, as well as reduce the risk of other complications such as stroke.
Blood transfusions: In severe cases of sickle cell disease, blood transfusions may be necessary to replace damaged red blood cells.
Bone marrow transplant: In some cases, a bone marrow transplant may be recommended to replace the faulty stem cells that produce sickle-shaped red blood cells.
Living with sickle cell disease can be challenging, but with proper management and care, people with this condition can lead healthy and productive lives.
It’s important for people with sickle cell disease to receive regular medical care and follow a treatment plan developed by their healthcare provider.
Conclusion
Sickle cell disease is a genetic blood disorder that can cause a wide range of symptoms, from mild to severe.
While there is no cure for sickle cell disease, there are treatments available that can help manage symptoms and prevent complications.
If you or someone you know has sickle cell disease, it’s important to seek medical care and follow a treatment plan to help manage this condition.